- Home
- Technical Tools
Technical Tools
Finding the technical information you want is often harder than it should be. To help you find 'what you need, when you need it', we’ve developed this online resource containing useful Standards, Charts and Calculators. And remember if it’s not here our in-store experts are always happy to answer any technical queries you may have.
Technical Tools Disclaimer
The information provided in this website is provided as a guide only. Reece Ltd does not warrant or accept liability in relation to the accuracy of this information. Individual users should make their own assessment of the information provided.
Reece Ltd reserves the right to change specifications, designs and availability without prior notice. Due to limitations in computer displays the colours in this website are a guide only. Reece Ltd accepts no responsibility for possible errors or omissions.
The use of the information on this website is subject to the terms and conditions found on this website.
Use this Unit Converter for a range of metrics including Temperature, Area, Pressure, Flow, Power and more. Click the drop down 'Select category' to get started.
The calculator below will allow you to select the appropriate cable size for your outdoor lighting system.
Finding the technical information you want is often harder than it should be. To help you find 'what you need, when you need it', we’ve developed this online resource containing useful Standards, Charts and Calculators. And remember if it’s not here our in-store experts are always happy to answer any technical queries you may have.

A
Extra Light Duty
Traffic
Areas (including footways) accessible only to pedestrians and pedal cyclists and closed to other trafficServiceability Design Load (kN)
6.7Ultimate Limit Design Load (kN)
10Nominal Wheel Loading (kg)
330
B
Light Duty
Traffic
Areas (including footways and light tractor paths) accessible to vehicles (excluding commercial vehicles) or livestockServiceability Design Load (kN)
53Ultimate Limit Design Load (kN)
80Nominal Wheel Loading (kg)
2,670
C
Medium Duty
Traffic
Malls and areas open to slow moving commercial vehiclesServiceability Design Load (kN)
100Ultimate Limit Design Load (kN)
150Nominal Wheel Loading (kg)
5,000
D
Heavy Duty
Traffic
Carriageways of roads and areas open to commercial vehiclesServiceability Design Load (kN)
140Ultimate Limit Design Load (kN)
210Nominal Wheel Loading (kg)
8,000
E
Extra Heavy Duty
Traffic
General docks and aircraft pavementsServiceability Design Load (kN)
267Ultimate Limit Design Load (kN)
400Nominal Wheel Loading (kg)
13,700
F
Extra Heavy Duty
Traffic
Docks and aircraft pavements subject to high wheel loadsServiceability Design Load (kN)
400Ultimate Limit Design Load (kN)
600Nominal Wheel Loading (kg)
20,000
G
Extra Heavy Duty
Traffic
Docks and aircraft pavements subject to very high wheel loadsServiceability Design Load (kN)
400Ultimate Limit Design Load (kN)
600Nominal Wheel Loading (kg)
20,000Selecting an appropriate cover or grate also depends on the where it will be installed and the various types of traffic that it may receive. Whilst load classifications provide a guide, nominal loads are based on stationary loads, which poorly simulate real world traffic conditions.
Also Consider

Dynamic Loads
Areas subject to moving traffic will exert a dynamic load which will try to twist a cover out of position. If traffic moves quickly or turns on a cover, a higher load class should be selected and extra design features should be sought such as slotted drainage, locking grates down with bolts or steel reinforcement.
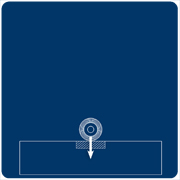
Small or Solid Wheels
Small or solid wheels concentrate a heavy load to a very small point where it is transferred to the cover. This can be the case with forklifts and rubbish skips which often feature solid wheels and cause massive damage to underspecified covers. A grate or cover with a higher load class will be required in these situations.
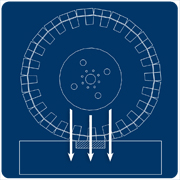
Large or Pneumatic
Large or pneumatic wheels will spread a load over a larger area and exert a lower stress on the grate or cover. This is why a heavy tractor can be classified in load class B with smaller vehicles.
Areas at the base of a steep decline
Covers at the base of a decline will experience short periods of increased load as a large portion of the vehicles total weight can be transferred to the front wheels. The cover will be under high stress and a higher load class will be required in these situations.
Notes
- Nominal wheel loads are given for guidance only. Consideration should be given to the type, size and pneumatic pressure of the load applied.
- Class B design loads exceed AS 5100.2 requirements for footway loading.
- Class D design loads exceed AS 5100.2 requirements for a W80 wheel load.
- Class C units are based on an intermediate load.
- The serviceability load is set at 2/3 of the ultimate limit state design load.
- A force of 1 kN approximately equal to the weight of 100 kg.
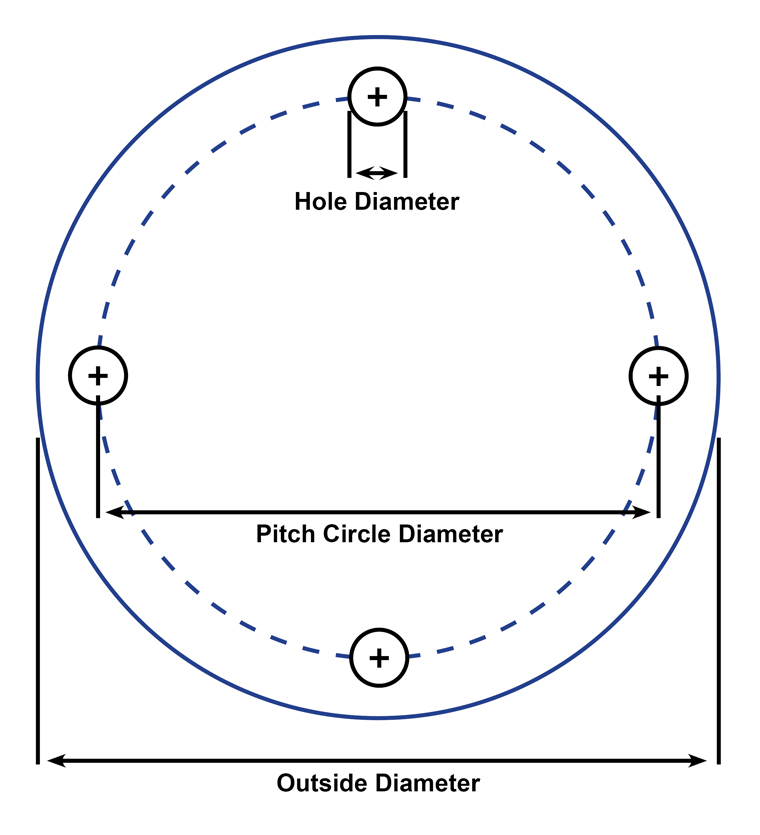
The Flange Dimensions Guide will help you easily find basic measurements and bolting information for many of the commonly used flange standards in Australia.
Option 1 - Search by Diameter
Option 2 - Search by Category